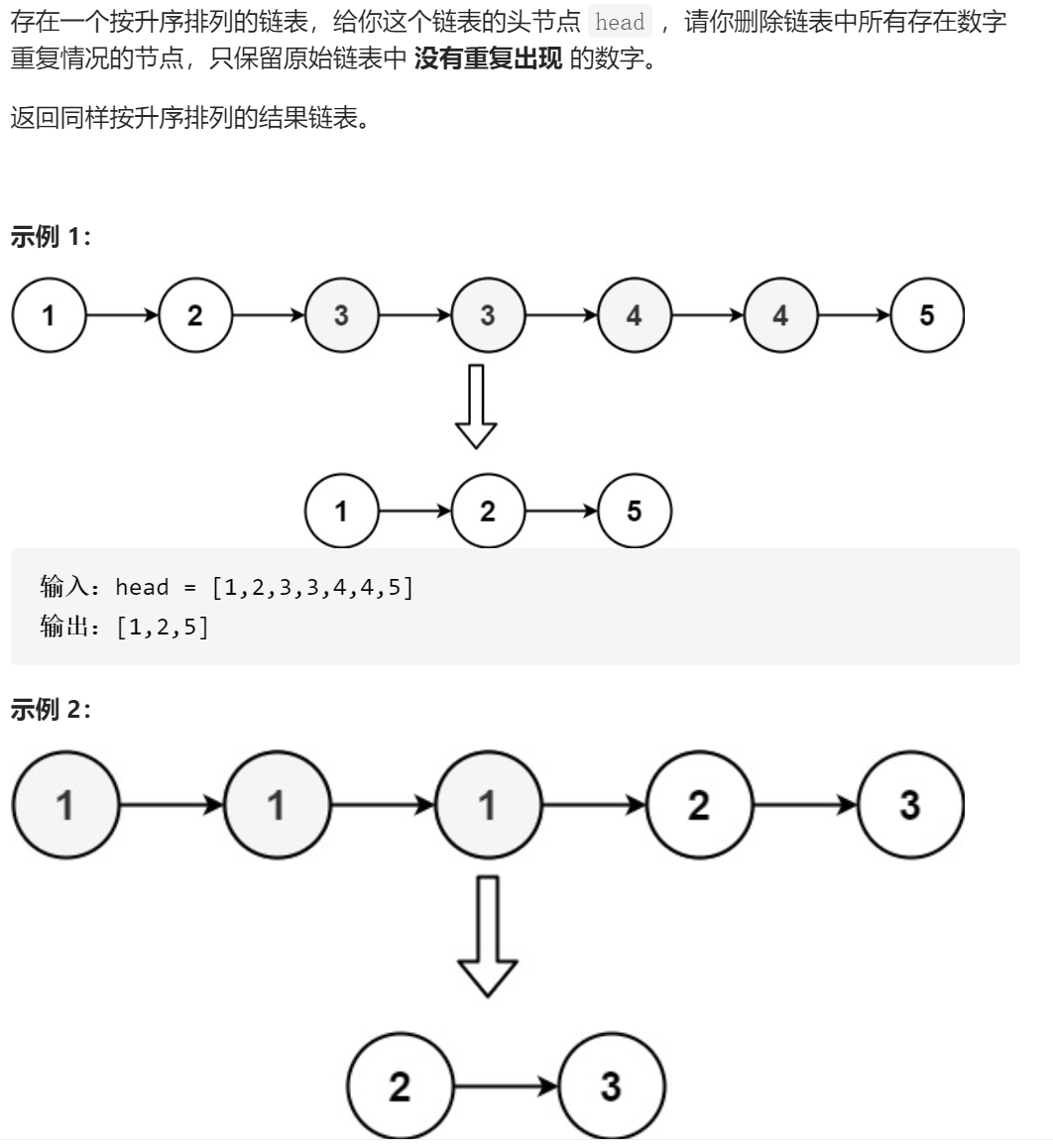
自己的做法
算法思想
因为有可能头节点是重复节点,所以方便删除,可以添加一个哨兵节点,即在头节点前再添加一个节点。
设置计数变量count,初始为1,如果有重复节点,则count >= 2。
设置pre指向访问过程中已知的最后一个不重复的节点,初始指向哨兵节点。
设置cur指针来遍历节点,初始指向头节点。
遍历链表,当当前链表的下个节点的值和当前节点的值相等时,就访问下个节点。同时计数变量count 加1。
如果不相等,有两种情况:
- count为1,说明不是重复节点,则将pre指向cur指向的节点,即
pre = cur,同时cur访问下一个节点 - count不为1,则说明是重复节点,应该删除。则令pre的next指向cur的next,同时计数变量重新置为1,并访问下个节点
注:(pre, cur]之间的为重复的节点,不包括pre,包括cur。
算法实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution {
public:
static ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) {return head;}
ListNode * sentinel = new ListNode();
sentinel->next = head;
ListNode * pre = sentinel;
ListNode * cur = head;
int count = 1;
while (cur) {
if(cur->next && cur->next->val == cur->val) {
count++;
} else {
if(count != 1) {
pre->next = cur->next;
count = 1;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return sentinel->next;
}
};
|
性能分析
时间复杂度:遍历一遍链表,O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
参考做法
算法思想
设置一个哑结点(dummy node,其实和哨兵节点一样,就是在头节点前加一个节点)。
设置指针cur,初始指向哑结点,然后判断cur->next和cur->next->next的值是否相等,
如果相等,那么就记录下该值x,并循环删除cur->next及其后面所有和x相等的值,直到cur->next为空或cur->next的值和x不相等;
如果不相等,那么就cur就指向下一个节点。
算法实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class Solution {
public:
static ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) {return head;}
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode();
dummy->next = head;
ListNode * cur = dummy;
while (cur->next && cur->next->next) {
if(cur->next->val == cur->next->next->val) {
int x = cur->next->val;
while (cur->next || cur->next->val == x) {
cur->next = cur->next->next;
}
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
|
性能分析
时间复杂度:O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
注:如果只是做题,可以不释放删除节点的内存,但在实际工作中,一定是要释放的。
