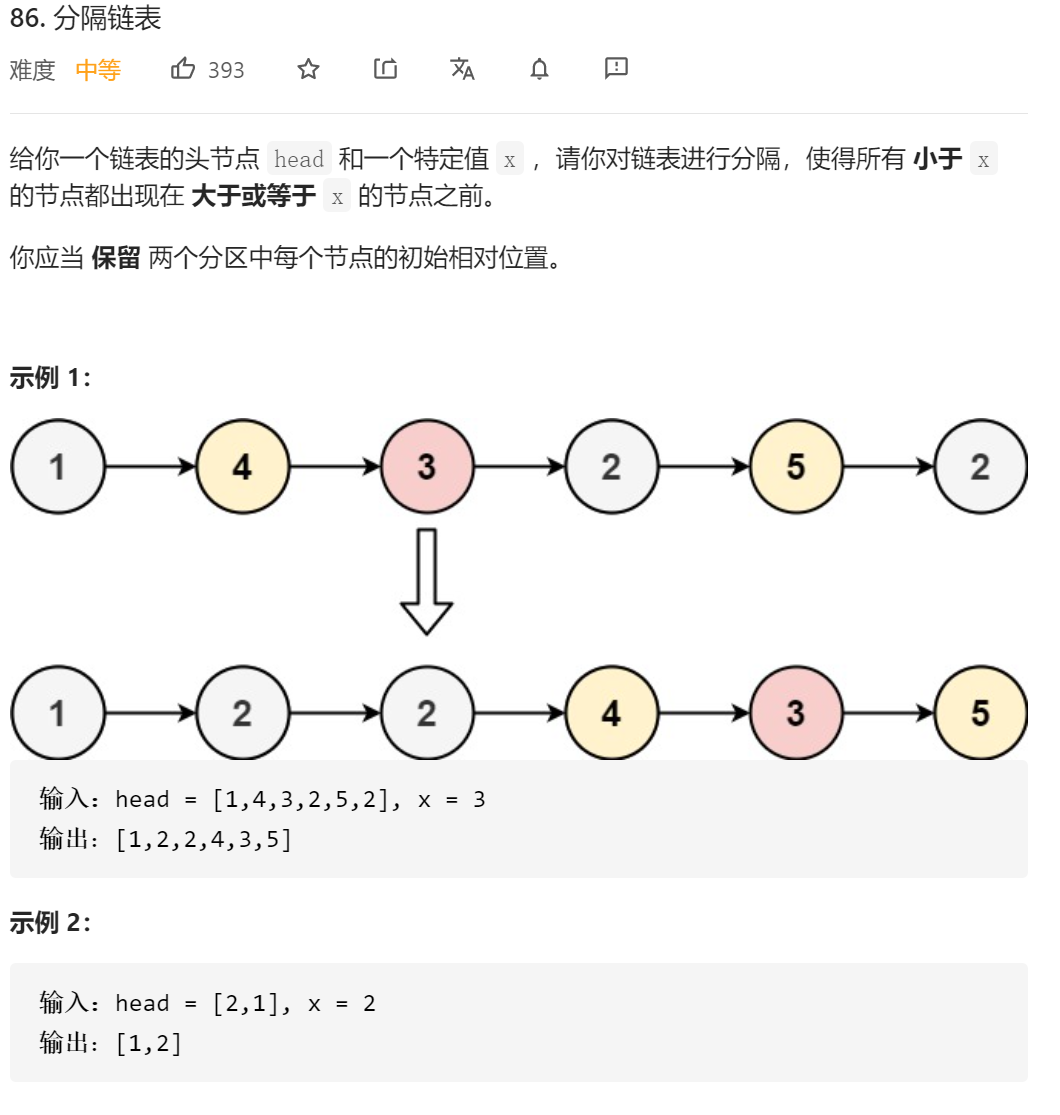
自己的做法
算法思想
遍历链表,将所有比x小的节点放到链表前面来。又要求相对位置不能改变,所以应将比x小的节点,放到所有比x小的节点组成的链表的末尾。
因为有可能添加的节点会放到链表头,所以添加哑节点(dummy node)。
所以设置指针less指向所有比x小的节点组成的链表的尾节点,初始指向哑节点。
设cur指针来遍历链表,初始指向头节点。
同时当将比x小的节点放到前面时,该节点的前一个节点的next也应该修改,所以添加一个指针pre指向cur的前一个节点。
同时注意,如果cur指向的节点小于x,但是该节点是less指针的下一个节点,即该节点已经在正确位置了,就不需要改动了。
算法实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) {return head;}
ListNode * dummy = new ListNode();
dummy->next = head;
ListNode * less = dummy;
ListNode * pre = dummy;
ListNode * cur = head;
while (cur) {
if(cur->val < x) {
if(less->next == cur) {
less = cur;
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
} else {
pre->next = cur->next;
cur->next = less->next;
less->next = cur;
less = cur;
cur = pre->next;
}
} else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
|
性能分析
时间复杂度:O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
参考做法
算法思想
模拟。
维护两个链表,一个比x小的链表small,一个比x大的链表large。最后将large链表放到small链表的后面即可。
创建两个哑节点,分别使用smallHead和largeHead指针来指向这两个节点,同时设置small和large指针来分别指向两个链表的尾节点,初始时这两个指针同样指向各自的哑节点。
然后遍历链表,如果小于x,则放到small指向的节点后面,然后small指针指向该节点;
如果大于x,则放到large指向的节点后面,然后large指针指向该节点。
便利结束后,将两个链表连接起来即可。
算法实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) {return head;}
ListNode * smallHead = new ListNode();
ListNode * largeHead = new ListNode();
ListNode * small = smallHead;
ListNode * large = largeHead;
while (head) {
if(head->val < x) {
small->next = head;
small = small->next;
} else {
large->next = head;
large = large->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
large->next = nullptr;
small->next = largeHead->next;
return smallHead->next;
}
};
|
性能分析
时间复杂度:O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
