
自己的做法
算法思想
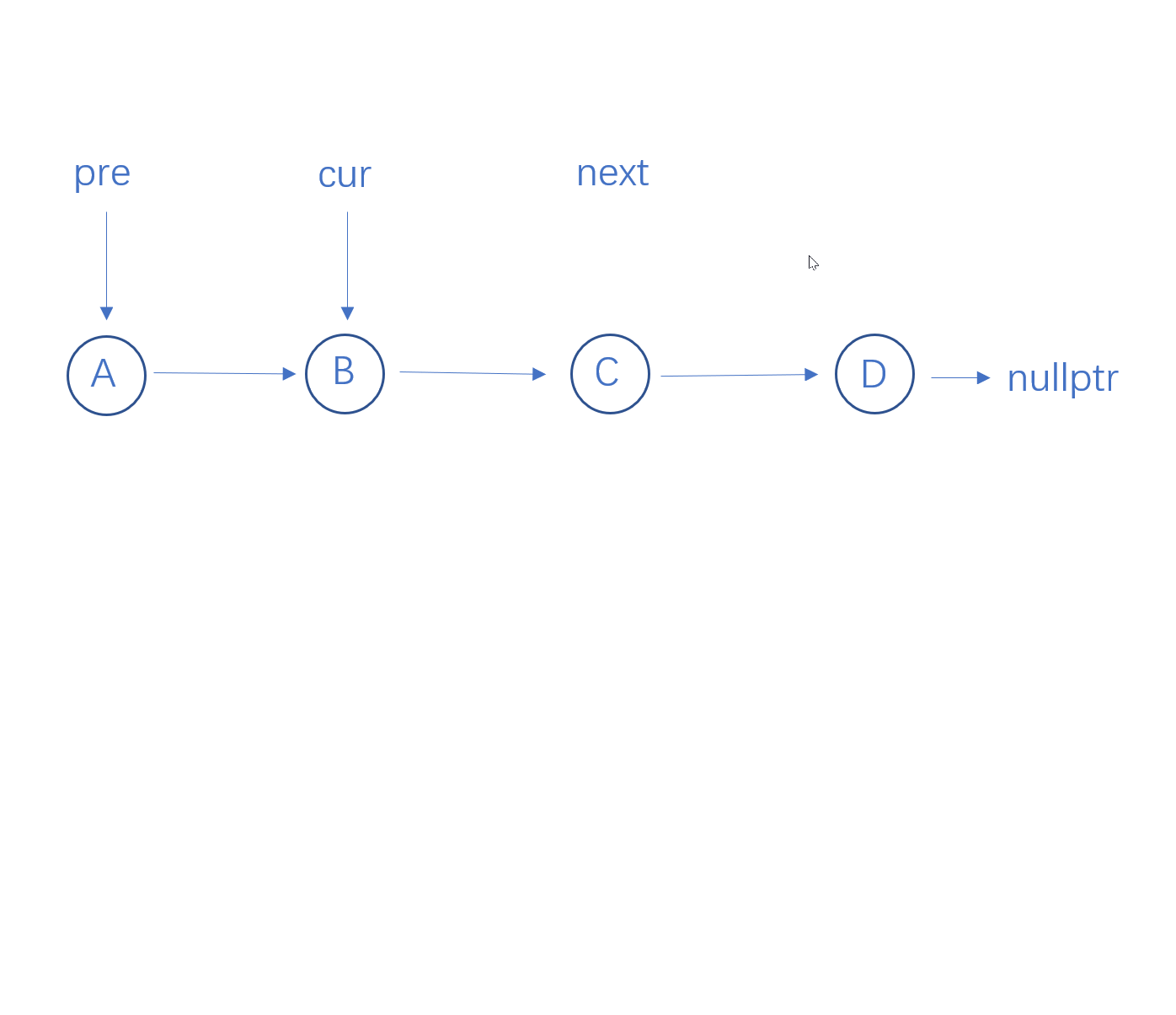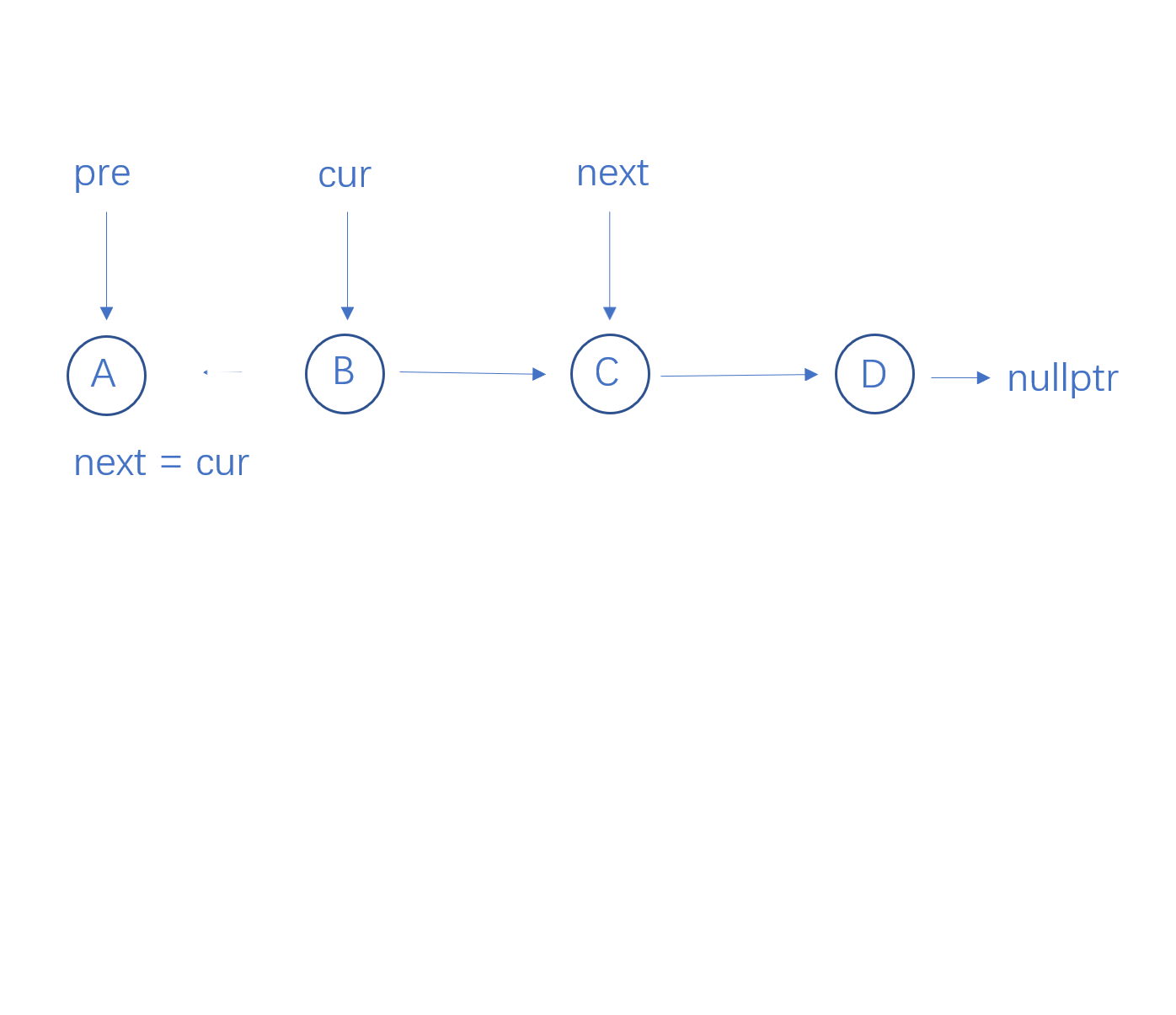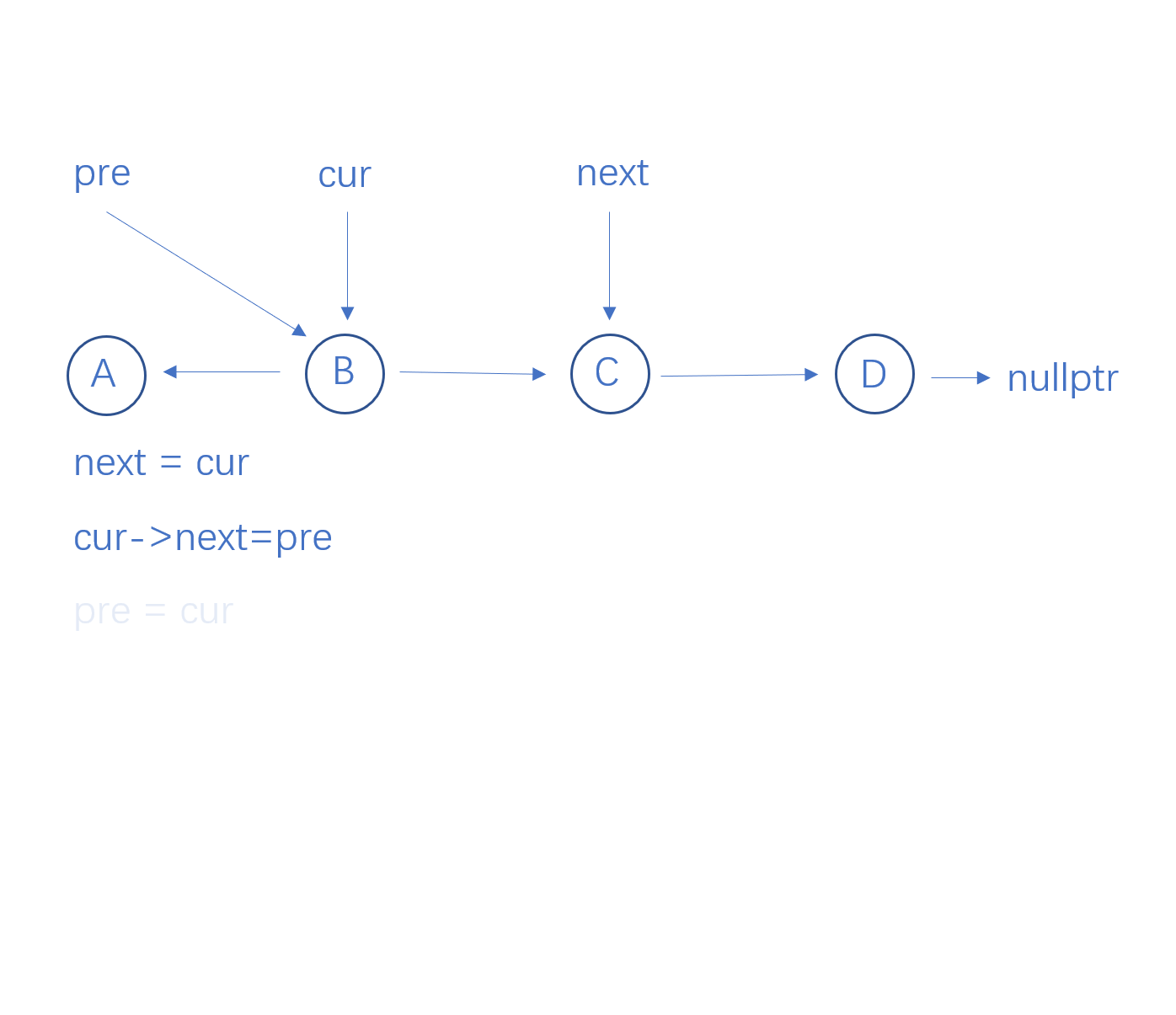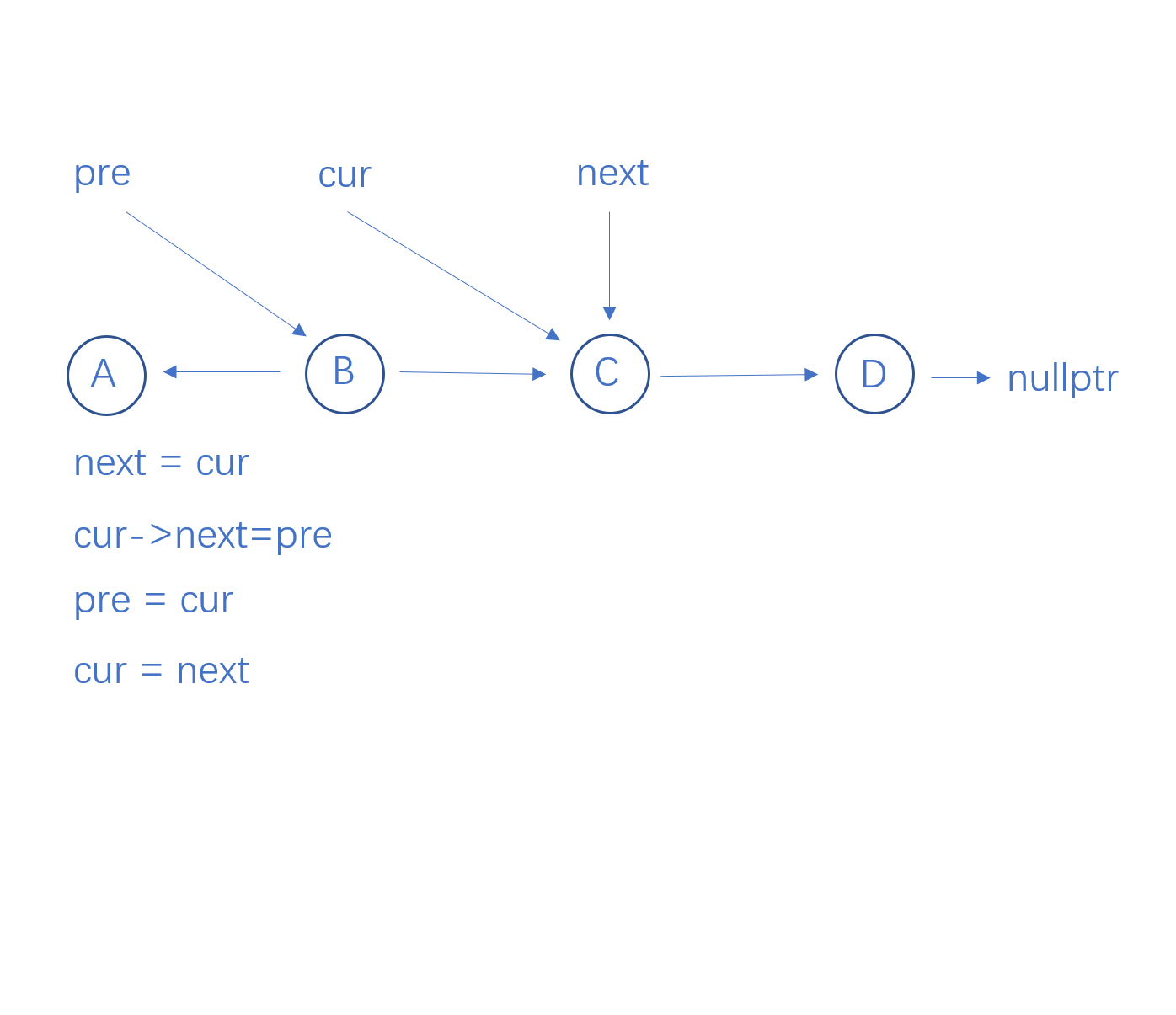
使用三个指针cur、pre和next,遍历链表。cur代表当前指向的结点,pre代表当前cur的前一个结点,next代表cur的后一个结点。
初始时,cur指向head->next即链表第二个结点,pre指向head,即头结点。next为空指针。
然后依次执行以下步骤:
next结点指向cur的下一个节点
cur结点的next指向pre结点
pre结点指向cur结点
cur指向next节点
这样就将pre和cur指向的结点进行了反转,并指向了下一个要反转的结点。
直到cur指向了空,此时循环结束,链表反转完成。
注:
算法实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) {return head;}
ListNode * pre = head;
ListNode * cur = head->next;
ListNode * next = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr) {
if(pre == head) {
pre->next = nullptr;
}
next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
|
还有一种更简单的写法,省去了判断链表结点数是否大于等于2和pre == head的情况。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode * pre = nullptr;
ListNode * cur = head;
ListNode * next = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr) {
if(pre == head) {
pre->next = nullptr;
}
next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
|
性能分析
时间复杂度为O(n)。
空间复杂度:用了三个指针,O(1)。
官方做法
递归
算法思想
从链表头结点递归到最后一个结点,然后进行回溯,当head指向一个结点时,要让它的下一个结点指向它,则需要执行head->next->next = head, 并让head结点的next指向空。
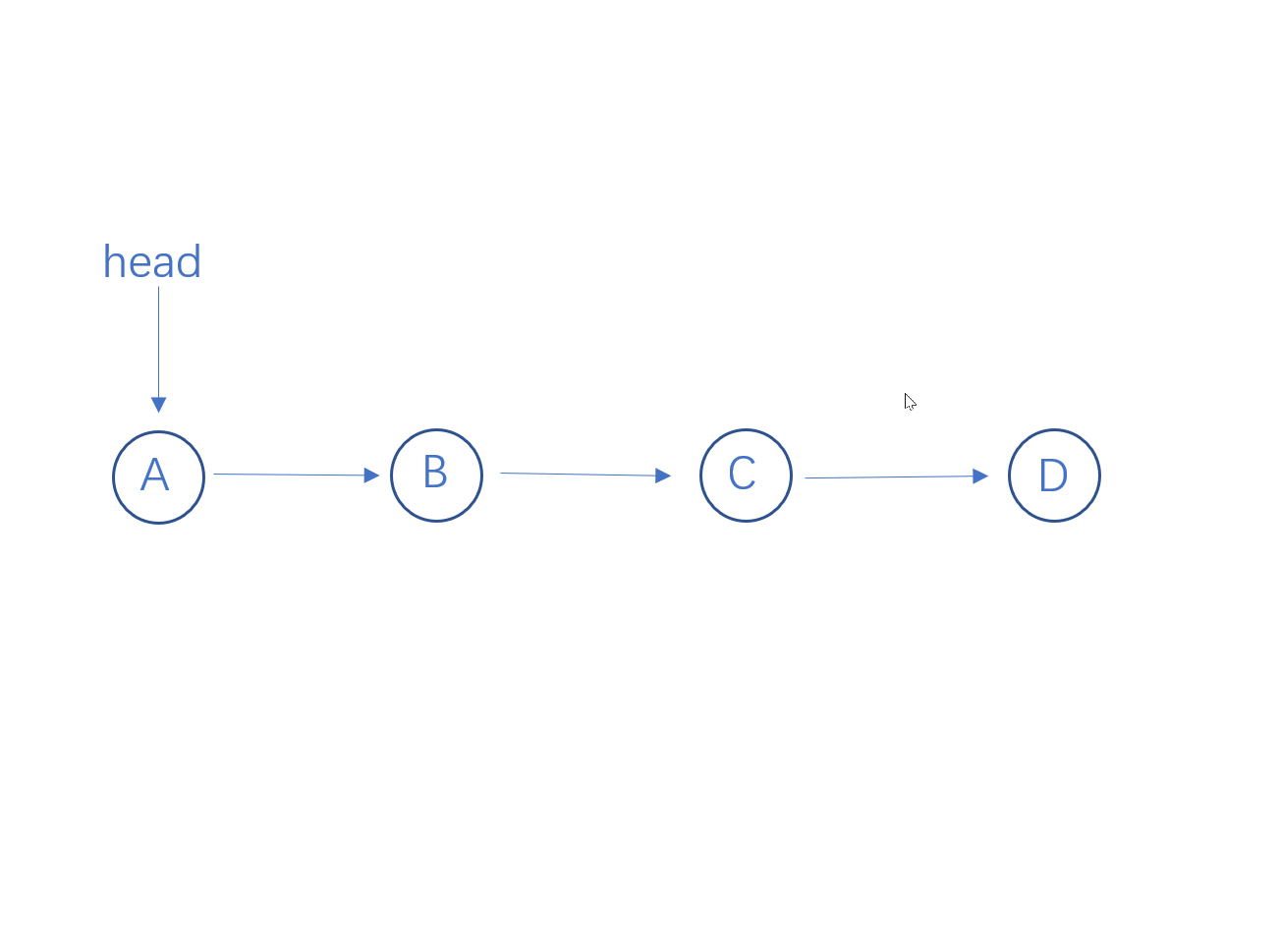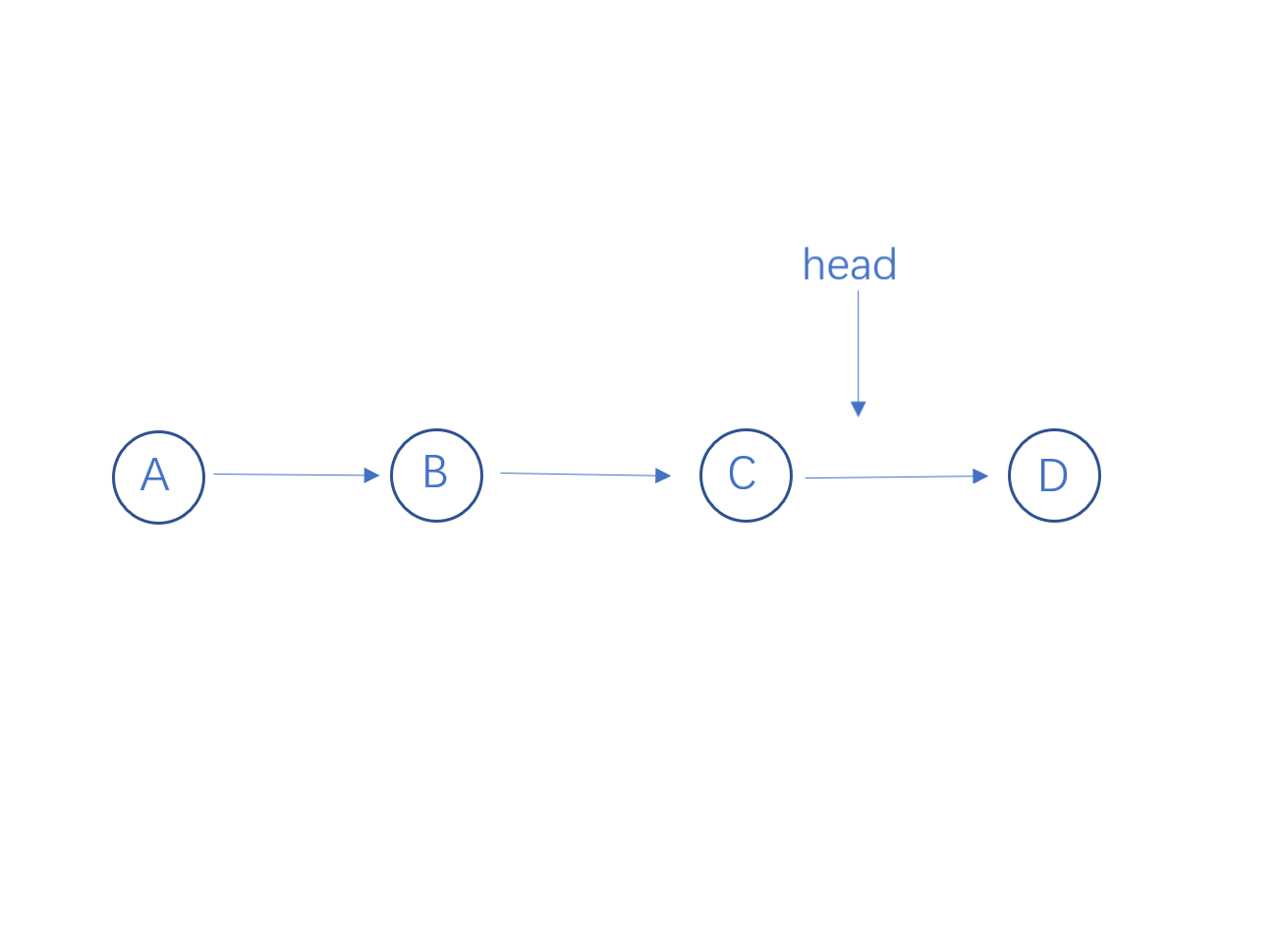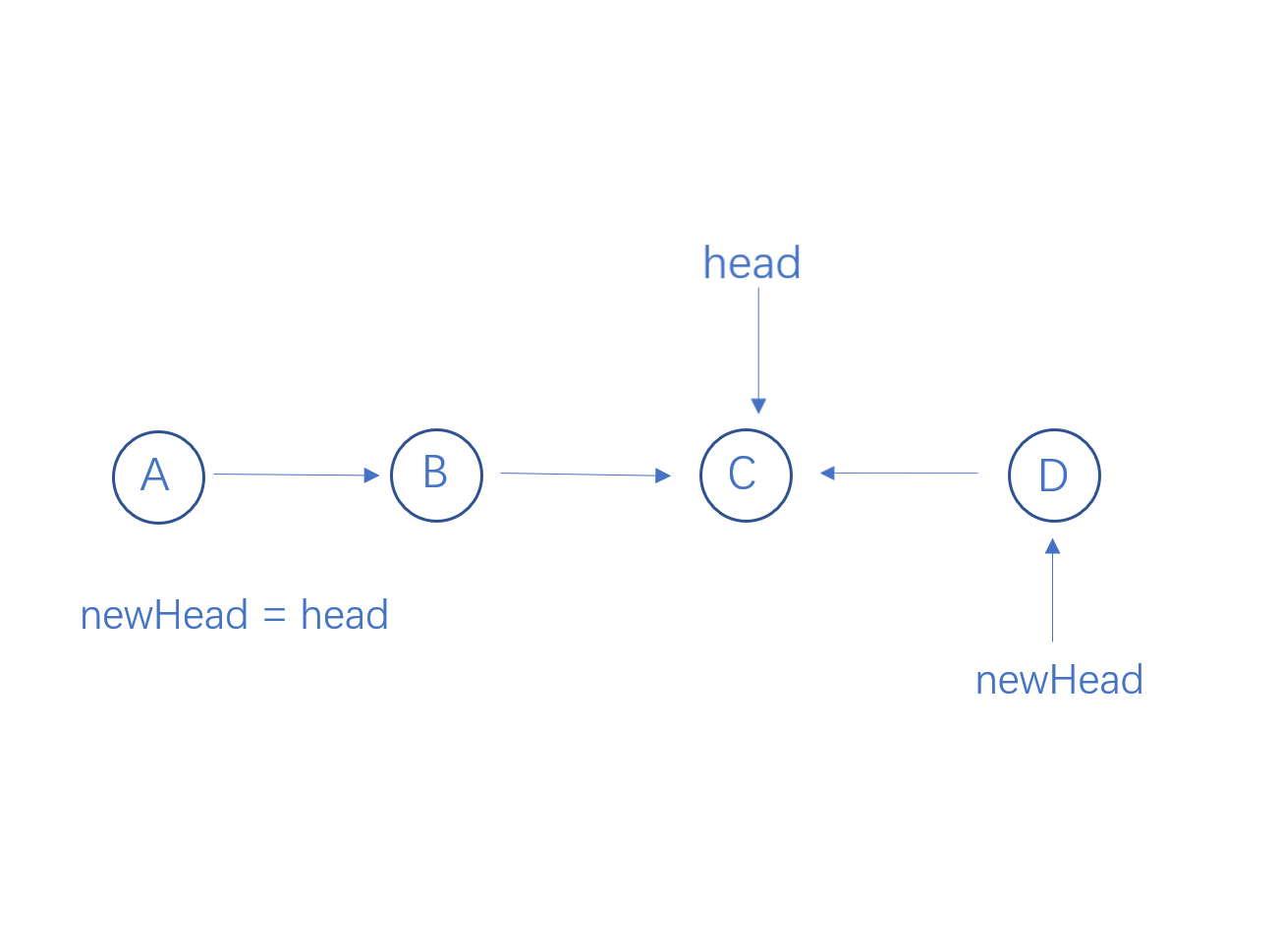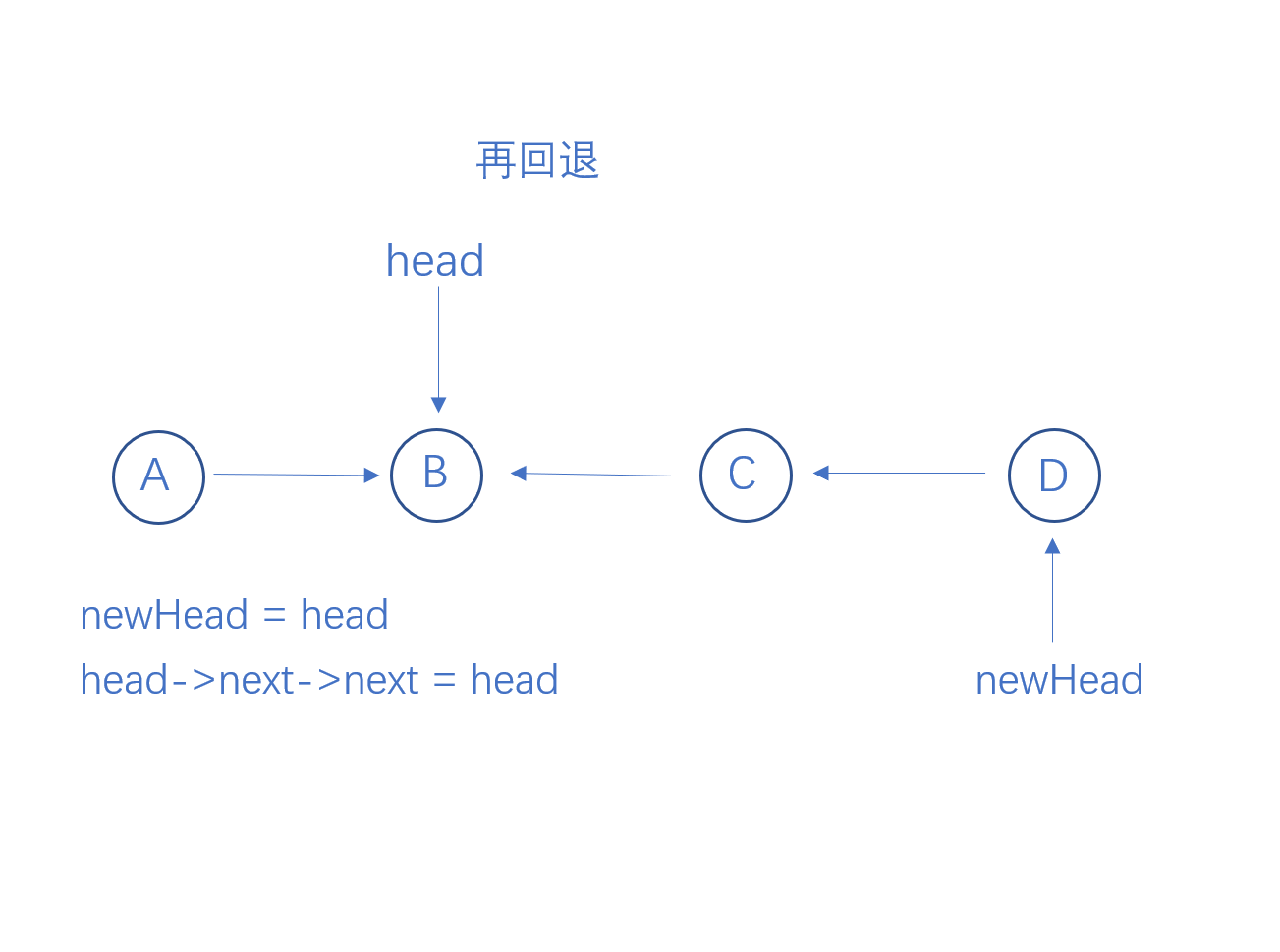
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) {return head;}
ListNode * newHead = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
return newHead;
}
};
|
性能分析
时间复杂度:O(n)。
空间复杂度:每次递归都需要将当前变量压栈,为O(n)。


